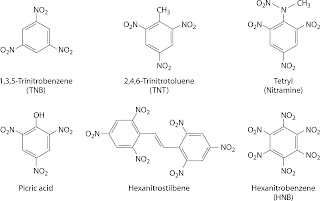
- Nitroaromatics are common military explosives such as Trinitro toluene-TNT, solvents such as nitrobenzene and pesticides such as nitro phenols.
- Nitrosubstitution of aromatic rings decreases biodegradability.
- These compounds are highy toxic and mutagenic
- Compounds with several nitrosubstituents are recalcitrant
- Biodegradation of nitroaromatic compounds tend to be slow and leads to bound or polymerized residues in soils and sediments
- Extensively nitro-substituted aromatics are more easily transformed under anaerobic conditions than aerobic conditions.
Oxidative pathway/Aerobic
- Nitrobenzene is converted to diol by the action of dioxygenases which gets converted to catechol. Catechol ring is opened by meta-cleavage later.
- Nitrobenzene dioxygenaseàNitrobenzene diolà Catechol (ring opening by metacleavage) àoxalocrotonaldehyde--àOxalocrotonate
Reductive pathway/Anaerobic
- Release
more energy
- Does
not require strict anaerobic conditions
- Nitro
group is stepwise reduced through nitrobenzene to phenylhydroxylamine to
2-aminophenol. The phenol ring subsequently opens up and oxalocrotonate is
formed with the release of ammonia
Trinitro toluene -TNT
- no efficient biodegradation pathway
- Under anaerobic and microaerophilic conditions, nitro groups of TNT are reduced one by one to amino groups, each subsequent reduction slower and less complete
- If conditions are aerobic, the partially reduced intermediates form very complex and mutagenic azo condensation products
- No mineralization, but only polymerization or binding of residues




No comments:
Post a Comment