Biochemical Reactions
- · Catalase and oxidase negative
- · Ferments sugars with acid production -Fermentation tested in Hiss’s serum water **
- · Ferments Inulin-streptococci does not
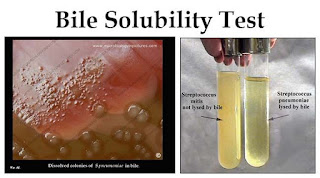
- · Pneumococci are bile soluble-of diagnostic importance
- · Bile solubility test: If a few drops of 10% sodium deoxycholate are added to 1 mL of an overnight broth culture, the culture clears due to lysis of cocci- due to an autolytic amidase that cleaves the bond between alanine and muramic acid in the peptidoglycan; Amidase is activated by bile salts
**(
Resistance
- · Pneumococci are delicate organisms.
- · Readily destroyed by heat- 52° C for 15 minutes and antiseptics
- Cultures die on prolonged incubation due to accumulation of toxic peroxides- maintained by lyophilisation
- · Sensitive to beta lactam antibiotics initially- now resistant-resistance due to alteration in penicillin binding proteins on the bacterial surface
- · Pneumococci sensitive to Optochin (Ethyl hydrocuprein) sensitive- Streptococci are not
Toxins and Virulence Factors
- · Virulence depends on its capsule and the production of a toxin called pneumolysin
- · Capsular Polysaccharide (acidic & hydrophilic) - protects the cocci from phagocytosis
- · Enhanced Virulence of type 3 due to abundant capsular material- Non capsulated strains are avirulent - Antibody to capsular polysaccharide is protective
- · Pneumolysin –membrane damaging toxin produced by Pneumococci- cytotoxic and complement activating properties- virulence factor-immunogenic
- (Pneumolysin-negative mutants showed less virulence in experimental animals)
- · Pneumococcal Autolysins- release bacterial components in infected tissues- contribute to virulence
- Oxygen labile hemolysin and leucocidin – not significant in virulence




No comments:
Post a Comment